Spiral Model
Introduction
The spiral model is a combination of sequential and prototype models. This model is best used for large projects which involve continuous enhancements. There are specific activities that are done in one iteration (spiral) where the output is a small prototype of the large software. The same activities are then repeated for all the spirals until the entire software is built.
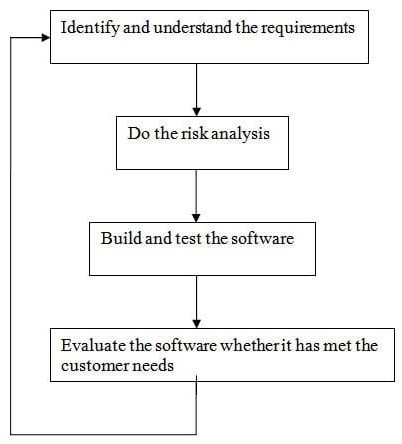
Phases
A spiral model has 4 phases described below:
- Planning phase.
- Risk analysis phase.
- Engineering phase.
- Evaluation phase.
When to Use?
Spiral model is used in the following scenarios:
- When the project is large.
- Where the software needs continuous risk evaluation.
- Requirements are a bit complicated and require continuous clarification.
- Software requires significant changes.
- Where enough time frame is their to get end user feedback.
- Where releases are required to be frequent.
Advantages
Advantages of using Spiral model are as follows:
- Development is fast
- Larger projects / software are created and handled in a strategic way
- Risk evaluation is proper.
- Control towards all the phases of development.
- More and more features are added in a systematic way.
- Software is produced early.
- Has room for customer feedback and the changes are implemented faster.
Disadvantages
Disadvantages of Spiral model are as follows:
- Risk analysis is important phase so requires expert people.
- Is not beneficial for smaller projects.
- Spiral may go infinitely.
- Documentation is more as it has intermediate phases.
- It is costly for smaller projects.